Last Updated on September 23, 2023
Are you worried about SharePoint security?
In this article, you will learn the basics of SharePoint security, known risks and vulnerabilities, common misconfiguration, and risk mitigation.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents:
- The Basics of SharePoint Security
- Known Risks and Vulnerabilities
- Common Misconfigurations Leading to Vulnerabilities
- Mitigating the Risks: Best Practices
- 1. Regularly reviewing and updating permissions
- 2. Staying updated with patches and security advisories
- 3. Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users
- 4. Training users on the importance of security and best practices
- 5. Implementing data loss prevention (DLP) policies
- 6. Monitoring and analyzing logs for suspicious activities
- 7. Backing up data and having a robust recovery plan in place.
- Sharepoint Security: The Answer
Understanding SharePoint’s intrinsic security measures is important for anyone managing or working with this platform.
Why? Well, security is like an invisible fortress for your data, and you would always want to know how strong that fortress is.
Here are what SharePoint offers you right out of the box:
Out-Of-The-Box Security Features
Starting with the default security settings:
1. Role-based access control
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific resources based on their roles within your organization.
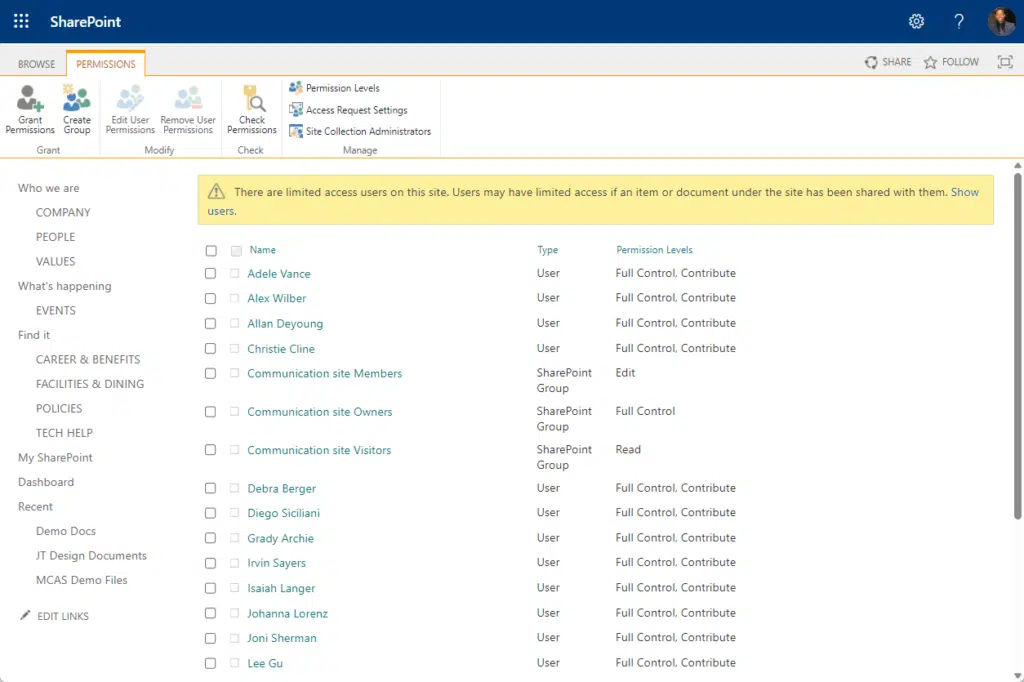
Why is it important for you?
- It simplifies administration: You don’t have to individually assign permissions for every user. Instead, assign them a role, and SharePoint will handle the rest.
- Minimizes accidental data leaks: Even if someone wants to share a document, if they don’t have the right role, they can’t. It’s as straightforward as that.
- Ensures accountability: Knowing who has access to what can simplify audit trails.
A good example of a situation where this feature shines the most is when an employee unintentionally deleted crucial project files.
With RBAC in place, such mishaps can be significantly minimized, as not everyone would have permission to modify or delete important content.
2. Data encryption in transit and at rest
Encryption ensures your data remains a jumble of unreadable characters unless someone has the correct decryption key.
“In transit” means while data is moving (like during an email exchange), and “at rest” means while data is stored.
How does it benefit you?
- Protects sensitive information: If someone intercepts your data, without the right key, all they see is gibberish.
- Complies with regulations: Many industries require data encryption. SharePoint helps you meet those standards effortlessly.
Related: How to Create Sensitivity Labels in Microsoft 365
3. Auditing and monitoring tools
These are tools that track user activities and system changes. Think of them as CCTV for your data.
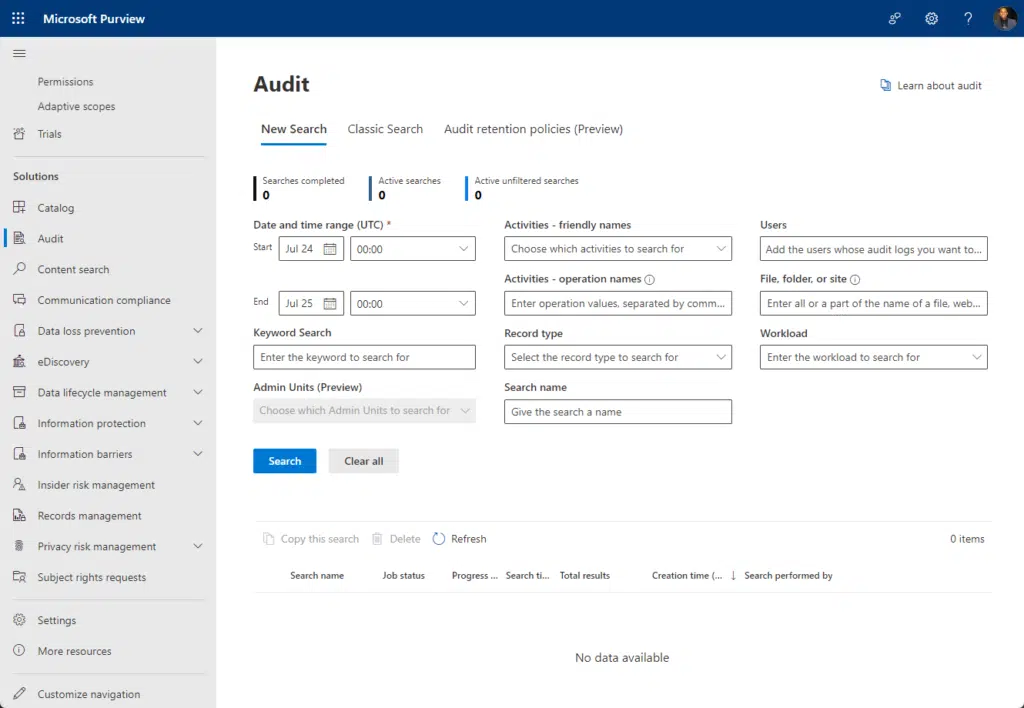
Why you should care:
- Keeps you informed: Know who accessed what, when, and what changes they made.
- Assists in anomaly detection: Spot unauthorized or unusual activities quickly.
- Helps in compliance: Many industries require detailed audit logs.
Integration With Other Microsoft Security Products
Microsoft, recognizing the importance of holistic security, has designed SharePoint to integrate seamlessly with its other security products.
This means an enhanced security umbrella for your data.
- Azure AD (Azure Active Directory):
- Offers identity services, ensuring only authenticated users can access your resources.
- Provides multi-factor authentication (MFA), adding an extra layer of protection.
- When you integrate SharePoint with Azure AD, managing user identities and permissions becomes a breeze.
- Microsoft Information Protection:
- Helps classify and protect documents and emails based on their sensitivity.
- You can set policies that restrict the actions that can be taken on items. For instance, you might prevent an email from being forwarded or a document from being printed.
- With SharePoint, this ensures that sensitive documents retain their protection settings even if they are shared outside your organization.
By leveraging these integrations, you increase SharePoint’s innate security, providing a robust defense framework.
Sign up for exclusive updates, tips, and strategies
Known Risks and Vulnerabilities
When you’re trusting a platform like SharePoint with your essential data, understanding its vulnerabilities is as crucial as recognizing its strengths.
By understanding past mistakes and current vulnerabilities, you can navigate the digital world with increased security.
Past Security Breaches and Vulnerabilities
It’s said that history often repeats itself, especially if lessons aren’t learned.
Reflecting on past security challenges faced by SharePoint can offer insights into areas of focus for your own security measures.
- Early version challenges: Initial versions of SharePoint (circa 2001-2003) had issues related to permissions inheritance, making data leakages a tangible concern.
- Misconfigurations: Over the years, numerous instances were reported where SharePoint sites were misconfigured, leading to unintentional data exposure. This wasn’t a flaw in SharePoint but rather a result of incorrect setups.
- Third-party integrations: In some instances, third-party plugins and integrations created vulnerabilities within SharePoint, leading to breaches.
Current Vulnerabilities
Staying updated on current vulnerabilities is paramount.
Specific vulnerabilities and their potential impact:
- Security misconfigurations
- Improper setup of SharePoint’s settings and permissions.
- Unintentional data exposure, loss of data integrity, and possible data breaches.
- Insecure direct object references (IDOR):
- When an attacker can access a reference to an internal implementation object, like files or database entries.
- Unauthorized data access, potential data manipulation, or deletion.
Publicly disclosed breaches and their consequences
While discussing specifics can be sensitive, it’s important to recognize the implications of major breaches.
This is for both the businesses affected and the users trusting them:
1. UN Breach
- Details: In 2019, hackers used a Microsoft SharePoint vulnerability (CVE-2019-0604) to access over 40 UN servers in Geneva and Vienna. The UN IT team missed a patch from Microsoft that could have prevented this. Sensitive data, including ‘active directories’ and HR systems, were downloaded.
- Consequences: About 4,000 staff in three offices were impacted. They were told to change passwords but weren’t informed about the data breach. The UN’s non-disclosure might erode trust in its data security and transparency. The attackers’ identity is unknown, but the incident aligns with increasing nation-state cyberattacks.
2. Dragos CEO Ransomware Attack
- Details: Dragos CEO, Robert M. Lee, faced an extortion attempt when attackers compromised a new sales employee’s email before their start date. The attackers claimed to extract 130GB of data, including a government contract detail. Dragos’ internal systems remained secure due to role-based access controls (RBAC), and no ransom was paid.
- Consequences: The attackers, failing to use ransomware, threatened company executives and even called Lee’s family. Dragos openly shared details of the breach. The investigation continues, and while the potential data loss is concerning, Dragos aims to educate others on defense strategies. They’ve also enhanced their onboarding security measures.
While SharePoint offers a robust framework, it’s important to remain vigilant and stay updated on vulnerabilities.
- Always ensure that your SharePoint online security is up to par by frequently visiting the SharePoint admin center.
- Ensure that your SharePoint Online secure configurations are in place.
Common Misconfigurations Leading to Vulnerabilities
While SharePoint Online brings a lot to the table in terms of security, it’s not immune to human errors.
One of the most significant threats to your SharePoint environment isn’t always an external hacker — sometimes, it’s internal misconfigurations.
By understanding the most common mistakes, you position yourself to sidestep these pitfalls.
1. Inadequate user permissions settings
Understanding permissions is fundamental.
If not appropriately managed, permissions can be a backdoor into your secure environment.
- Broad permissions: Granting extensive permissions to users who don’t require them can lead to unintentional data exposure.
- Public links: External sharing of documents via public links without expiration dates means they’re accessible indefinitely.
- Lack of segmentation: Not segmenting data based on departments or roles can mean sensitive information is available to those who shouldn’t see it.
Related: SharePoint Permissions Explained: How Permission Levels Work
2. Lack of regular audits and reviews
Continuous audits and reviews aren’t just best practices — they’re necessities.
- Stale accounts: Not removing or updating permissions for employees who have left or changed roles can lead to potential vulnerabilities.
- Unchecked admins: Without regular checks in the security and compliance center, you might not realize an admin account has been compromised or is being misused.
- Outdated permission models: As businesses evolve, so do their data and access requirements. Not updating these models can leave you vulnerable.
Related: Microsoft Compliance Center: Microsoft Purview Basic Guide
3. Inconsistent or lax security policies
Without a clear and consistent security policy, even the best tools can fall short.
- No two-factor authentication (2FA): If you don’t mandate 2FA, even a strong password can be a weak link.
- Weak password policies: Not enforcing robust password standards can leave your systems easy to crack.
- Lack of user training: If your team isn’t educated about security risks, they can inadvertently become the weakest link.
4. Unpatched systems or delays in applying updates.
Updates and patches aren’t just about adding new features.
They often fix known vulnerabilities.
- Running outdated software: If you’re not on the latest version, you’re potentially exposed to known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
- Ignoring patch announcements: Not staying updated on security advisories means you might miss critical patches.
- Delay in deployment: Even if you know about an update, delaying its deployment can put your data at risk.
In essence, while SharePoint provides robust security tools, their efficacy depends on how they’re configured and maintained.
Being proactive, staying educated, and regularly updating your practices can help you ensure that your fortress remains impenetrable.
Mitigating the Risks: Best Practices
Security in SharePoint is not just about understanding potential risks but also about implementing proactive measures.
By adopting best practices, you’re not merely reacting to threats but staying one step ahead.
For more info, you can check out the article below:
Note: SharePoint Security: The Best Practices Guide for 2023
Here are some of the things you can do:
1. Regularly reviewing and updating permissions
Permissions are like gatekeepers to your data on your SharePoint site. Keeping them in check is essential.
Keeping them in check is essential. This is especially crucial when considering external users.
Learn from the principle of least privilege:
Grant users only the permissions they need to perform their job and nothing more. Assign permissions carefully to limit access and avoid potential threats.
Benefits:
- Minimized risk: Fewer people with access to sensitive data means reduced chances of data leaks.
- Improved accountability: With specific roles, it’s easier to track who did what.
Implementation Tips:
- Regular audits: Periodically review user roles and access levels.
- Automate where possible: Use tools that can suggest permission levels based on job roles.
2. Staying updated with patches and security advisories
An updated system is a more secure system.
- Regularly monitor: Stay connected with official SharePoint updates and security advisories.
- Schedule updates: Regularly schedule times to apply patches, ensuring minimal disruption while maximizing security.
3. Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users
MFA is like a double-check for user authenticity.
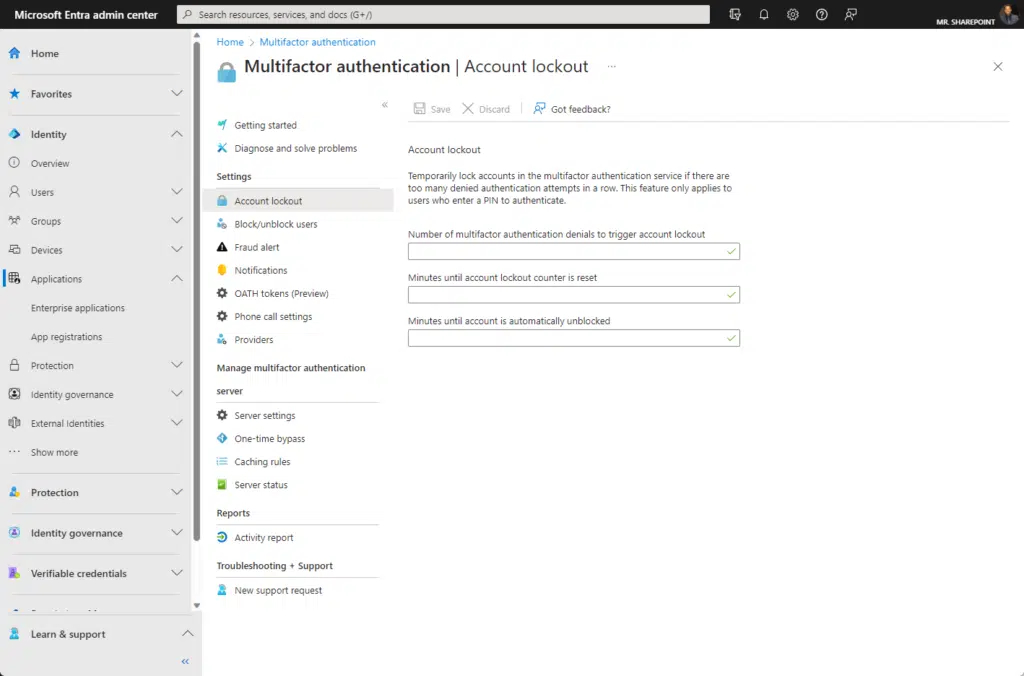
- It adds an additional layer of security, ensuring that even if passwords are compromised, your data isn’t.
- Implementation: Use tools within the Microsoft ecosystem to enable MFA for SharePoint users.
4. Training users on the importance of security and best practices
A well-informed team is your best defense.
- Host regular workshops: Keep your team updated on the latest security threats and how to avoid them.
- Simulate threats: Conduct mock phishing exercises to test and train your team’s responses.
5. Implementing data loss prevention (DLP) policies
Protect your data proactively:
- A strategy that ensures sensitive or critical data isn’t leaked outside the organization.
- SharePoint and DLP: Use SharePoint’s integrated tools to set up DLP policies, like preventing specific data from being emailed or shared.
Related: Microsoft Compliance Center: Microsoft Purview Basic Guide
6. Monitoring and analyzing logs for suspicious activities
Stay alert, always.
- Use SharePoint built-in tools: Monitor user activity, file access, and system changes.
- Integrate advanced solutions: Consider integrating solutions like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) for deeper insights.
7. Backing up data and having a robust recovery plan in place.
Always be prepared for the unexpected.
- Regular backups: Schedule daily or weekly backups of all SharePoint data.
- Test recovery processes: Periodically test your recovery processes to ensure they’re efficient and effective.
In the end, securing SharePoint is a combination of leveraging its in-built tools, staying updated, and fostering a culture of security awareness.
When these elements come together, you create an environment where data integrity and security take center stage.
SharePoint offers a robust set of built-in security features and integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft security tools.
However, its security is not just about built-in features but also how it’s configured and maintained.
Past vulnerabilities have been addressed by Microsoft through patches, but proper configuration, user training, and staying updated are crucial.
Basically, SharePoint is secure — but its overall security hinges on responsible management and user practices.
Do you still have any concerns or questions about security? If yes, feel free to leave a comment or two below.
If you need help with setting up security, kindly send me a message through the contact page, and let’s talk.


Thank you for this much needed information!