Last Updated on June 29, 2023
Need to add someone outside your organization to a group?
In this guide, I will show you the step-by-step process of adding an external user to a Microsoft 365 group, the permissions required, and more.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents:
- What is a Microsoft 365 group?
- How do external users differ from internal users?
- How to add external users to a Microsoft 365 group
- Did you encounter an issue when adding an external user?
- How do group external users differ from SharePoint external sharing?
- How does external access differ from guest access?
- Carefully manage external users in a Microsoft 365 group
What is a Microsoft 365 group?
For starters, a Microsoft 365 group is a shared workspace you can use for collaboration.
It brings together a team and allows them to share different resources:
- A collective email address
- Shared storage space for files
- A shared calendar
- A platform for team communication
The members of the group can access these resources to make it easier for them to work together.
You can also create two types of groups — public (seen by all users) and private (only approved users can see).
Related: Microsoft 365 Groups: Public vs Private (Differences)
Sign up for exclusive updates, tips, and strategies
How do external users differ from internal users?
Technically, an internal user is someone who has a licensed account within your organization.
This means they have an email address that ends with your organization’s domain (like ).
External users are the opposite — they don’t have a licensed account within your organization.
Typically, these people are partners, customers, or contractors who may or may not have their own Microsoft 365 license (from their organization).
Below is a table that highlights some key differences between an external user and an internal user:
| Internal Users | External Users | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | People with a licensed account in your organization | People outside your organization without a specific license from your organization |
| Email Address | Email ends with your organization’s domain | Email doesn’t end with your organization’s domain |
| Access to Resources | Can access all resources and applications provided by your organization’s Microsoft 365 subscription | Can be granted access to specific resources, like a document or a Microsoft 365 Group |
| Management | Managed by your organization’s IT department | Management depends on their own organization’s IT department or their individual settings |
Related: External Sharing in SharePoint Online: How Does It Work
How to add external users to a Microsoft 365 group
It’s quite easy to add external users to a Microsoft 365 group, though it may be a little confusing if you don’t about it yet.
That’s because this is done in Outlook and not in the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Pre-requisites for adding an external user
For the security of your organization, not everyone can add an external user.
You generally need to have the following permissions:
- Group ownership: As a group owner, you can manage the group’s settings, including adding or removing members.
- Administrator privileges: If you’re not the owner but have global admin/user admin roles, you can also add external users to any group.
- External sharing settings: This needs to be enabled in the Microsoft 365 admin center to allow sharing with external users (more on this later).
Related: SharePoint Permissions Explained: How Permission Levels Work
On the side of the external user, there is only one thing you need to add him or her — and that’s his or her email address.
The email address can be any valid one and it doesn’t have to be associated with a Microsoft account.
Step #1: Make sure adding external users is enabled
For this, you need to visit the Microsoft 365 admin center.
If you’re not sure how to do it, just go to any page in any app in Microsoft 365 and click the app launcher > admin button:

This will bring you to the homepage of the admin center.
From there, expand the settings options in the left-hand menu and then click on org settings:

This will bring you to various org settings.
Make sure you’re in the default tab (services) and find Microsoft 365 groups from the list:
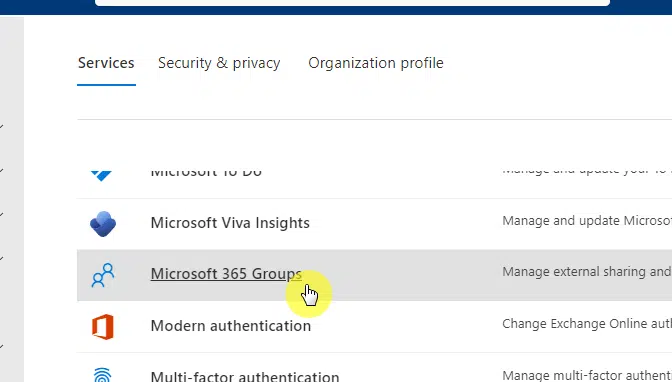
This will open a right-hand panel.
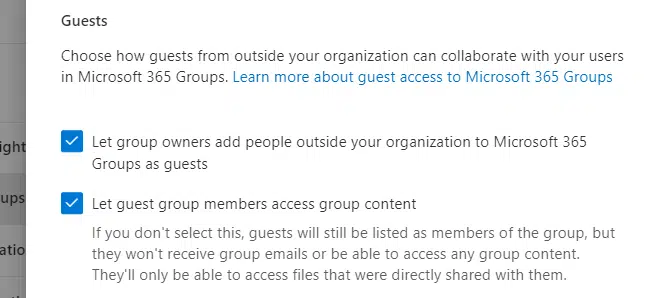
Make sure to select the first option and the second option (optional):
- Let groups owners add external users
- Let guest group members access group content
If you don’t select the second option, a guest user can only access files that were directly shared with them.
Hit the save button if you changed anything:
Related: How to Create a Microsoft 365 Group: The Ultimate List
Step #2: Add the external user from Outlook
In the second step, you need to open Outlook.
Select the group from the left-hand menu to which you want to add an external group member to.
Then click the number of group members:
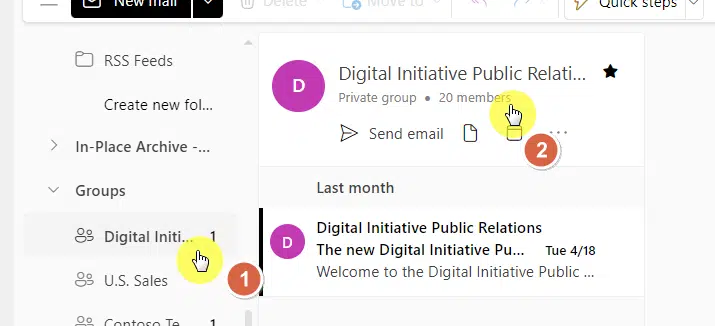
That will open a small window within Outlook.
The next step is to click the add members button:
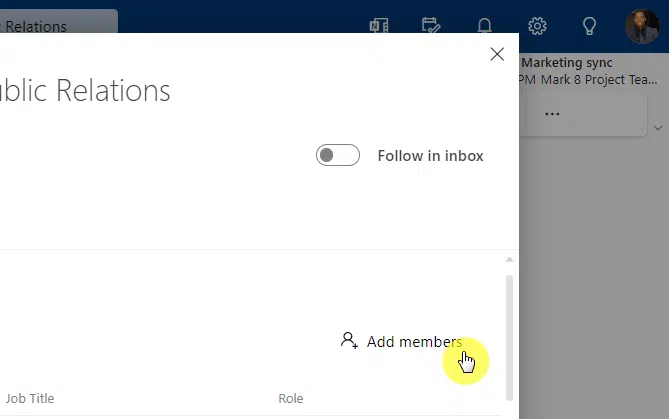
All you have to do now is enter the email address to invite external users to the group.
Click the add button:

The system will then send an email to the user to inform that his/her account was added to a specific group.
The email looks like this:
Did you encounter an issue when adding an external user?
There are only a few issues you may encounter when adding an external user to a Microsoft 365 group.
In fact, there are only three of them:
- Can’t add an external user
- External user didn’t receive an email
- External user can’t access group resources
For the first one, it’s possible that external sharing is disabled in your organization. Review step #1 in the section above.
For the second issue, double-check the email address you entered and ask the user to check their spam or junk email folder.
For the last one, ensure that the external user is signed in with the same email address where the invitation was sent.
If the problem still persists, there may be some technical issue that needs the expertise of your IT department.
Since both are in Microsoft, they are related — but not the same.
They are different methods of collaborating with people outside of your organization using Microsoft’s services and are used differently:
- Group external users, what we have been doing earlier, is adding an external user to a Microsoft 365 group.
- SharePoint external sharing refers to sharing specific SharePoint Online sites, folders, or files with an external user.
Here is a detailed table that can help illustrate the differences:
| Group External Users | SharePoint External Sharing | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding an external user to a Microsoft 365 Group. | Users have access to specific SharePoint sites, folders, or files that have been shared with them. |
| Access Level | Users have access to the shared resources of the group, including a shared mailbox, calendar, and file library. | Typically used for short-term sharing of specific documents or folders. |
| Long-term vs Short-term | Typically used for ongoing collaboration as part of a team or project. | Typically used for short-term sharing of specific documents or folders. |
| Management | Managed by the group owners or organization’s IT department. | Need to have the appropriate permissions for the SharePoint site, folder, or file you are sharing. |
| Permissions Required | Need to be an owner of the group or have administrative privileges. | Control over specific sites, folders, or files that have been shared. |
| Control Over Shared Resources | Control over the entire group’s shared resources. | Control over specific sites, folders, or files that have been shared. |
Related: External Sharing in SharePoint Online: How Does It Work
How does external access differ from guest access?
If you have been using Microsoft Teams, this may cause a little confusion.
In the context of Microsoft Teams, both external access (federation) and guest access are ways to collaborate with people outside your organization.
However, they are used for different purposes:
- External access allows users from an entire external domain to find, call, chat, and set up meetings with you in Teams
- Guest access is more about allowing guest users to have access to teams and channels and be part of charts, meetings, etc.
Below is a table to illustrate the differences:
| External Access (Federation) | Guest Access | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allows an entire external domain to find, call, chat, and set up meetings with you in Teams. | Grants an individual access to specific Teams, channels, and associated resources. |
| Access Level | Users have limited access to your organization’s Teams resources. They can communicate via chat, calls, and meetings. | Grants individual access to specific Teams, channels, and associated resources. |
| Access to Channels | No direct access to Teams channels. | Can access specific channels as permitted by the team owner. |
| Participation in Meetings | Can be invited to and participate in Teams meetings. | Can be invited to and participate in Teams meetings, and can schedule their own if allowed. |
| File Sharing | Cannot directly share files in Teams. | Can share files within specific channels they have access to. |
| Management | Managed by your organization’s IT department. | Can share files within specific channels they have access. |
| Use Case | Generally suitable for broad, inter-organizational communication. | Can access Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive for Business, and Office 365 Groups, as permitted. |
| Teams & Office 365 Services Access | Limited to Teams (and Skype for Business if still in use). | Can access Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive for Business, and Office 365 Groups, as permitted. |
Related: How to Add External Users to Microsoft Teams (Guest Access)
Carefully manage external users in a Microsoft 365 group
Before you go, I got some last-minute reminders that you can follow to keep your organization safe.
Here are some of the things you can do to manage external users:
- Keep a check on who has access – If someone’s role changes or they leave the company, make sure their access is updated or removed.
- Clear communication is key – Let the external users know what they have access to and what they’re expected to do.
- Regular clean-up – Remove external users who no longer need access to keep your group secure and manageable.
- Have a policy – Create a clear policy on who can add external users and when it’s appropriate to do so.
- Use adequate security measures – Ensure that sensitive information is protected so remind your team to not share sensitive data unless necessary.
- Be aware of licensing constraints – Some features might require a certain type of license, so it’s a good idea to avoid surprises.
Naturally, you don’t want those who shouldn’t have access to access to your Microsoft 365 group.
In addition, clear communication helps avoid confusion and makes collaboration easier. Make sure you’re aware as well of the limitations.
Every organization is different, so you might need to tweak some of these to fit your specific needs and situation.
It’s always a good idea to consult with your IT department or admins to make sure you’re following your organization’s guidelines.
I know — this was a simple topic, but there’s a lot to take in. If you need clarification, drop a question below.
For business inquiries and concerns, kindly send a message using the form here and I’ll get back to you asap.


I’m adding external top leaders but we don’t want them to get notified. Where/How do I add them?